IGNOU BCHCT-131 Solved Assignment 2024 | B.Sc. CBCS Chemistry
₹49.00
Please read the following points before ordering this IGNOU Assignment Solution.
Share with your Friends
IGNOU BCHCT-131 Assignment Question Paper 2024
bchct-131-solved-assignment-2024-35c75513-663a-4bae-bede-47f427737c46
-
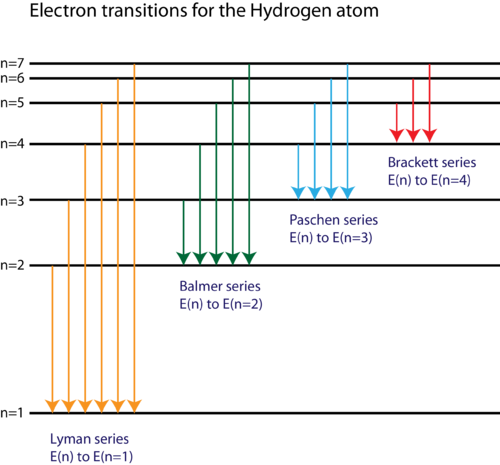
Using a suitable diagram explain the spectral transitions between different energy levels of hydrogen atom. Also name these series of lines and give the region of electromagnetic radiation in which they appear.
-
What was the purpose of Davisson and Germer experiment? Explains and analyse its results.
-
(a) What is a well-behaved wave function? Illustrate using suitable diagram.
-
What are different quantum numbers? Explain their significance.
-
Briefly explain the following:
(i) The aufbau principle
(ii) Hund’s rule
(iii) Pauli exclusion principle -
a) Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing lattice energy:
LiF,MgO,KBr \mathrm{LiF}, \mathrm{MgO}, \mathrm{KBr}
-
Why does the bond length decrease in the case of multiple bond formation? Explain with the help of an example. Also explain why a multiple bond is stronger than a single bond.
-
a) The observed dipole moment of
HI \mathrm{HI} 0.38D 0.38 \mathrm{D} HI \mathrm{HI} 161pm 161 \mathrm{pm}
-
Draw the resonance structures of carbon monoxide. Also give the electronic configuration of the combining atoms
-
Draw the energy level diagram for carbon monoxide molecule. Write its molecular orbitals configuration and calculate its bond order. Comment on its magnetic behaviour.
-
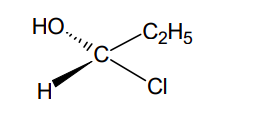
Draw all the stereoisomers of 2-bromo-3-chlorobutane and classify them as enantiomers and diastereoisomers.
-
(a) What are resolving agents? Give examples of three acidic and three basic resolving agents.
-
Draw and explain the energy propile for ring flipping of chair conformation of cyclohexane.
-
Arrange the following carbocations in the increasing order of stability and explain the reason for your answer:
A primary carbocation, a tertiary carbocation, a secondary carbocation. -
Arrange the following nucleophiles in the increasing order of their strength and give reason for your answer.
- (a) Define octane number. How does the octane number of a hydrocarbon vary with the following?
(i) Branching of the hydrocarbon chain
(ii) Decrease in the chain length
(iii) Unsaturation
-
How would you prepare an alkene using Wittig reaction? Explain the mechanism also.
-
What is Markownikoff’s rule? Explain using this rule why 2-bromopropane is the major product of bromination of propene.
-
Discuss different methods of preparation of propyne.
-
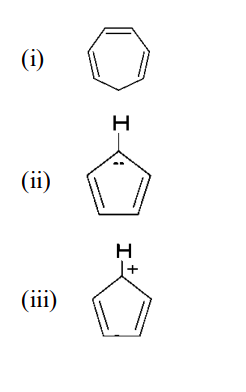
Explain whether the following compounds are aromatic or not?
BCHCT-131 Sample Solution 2024
bchct-131-solved-assignment-2024-ss-10cd7422-4b11-4531-9171-a6445826d855
- Using a suitable diagram explain the spectral transitions between different energy levels of hydrogen atom. Also name these series of lines and give the region of electromagnetic radiation in which they appear.
-
Lyman Series: Transitions from higher energy levels
n >= 2 n \geq 2 n=1 n = 1 -
Balmer Series: Transitions from higher energy levels
n >= 3 n \geq 3 n=2 n = 2 -
Paschen Series: Transitions from higher energy levels
n >= 4 n \geq 4 n=3 n = 3 -
Brackett Series: Transitions from higher energy levels
n >= 5 n \geq 5 n=4 n = 4 -
Pfund Series: Transitions from higher energy levels
n >= 6 n \geq 6 n=5 n = 5
-
Lyman Series: This series represents transitions from higher energy levels to the
n=1 n = 1 -
Balmer Series: These transitions occur from higher levels to the
n=2 n = 2 -
Paschen Series: Transitions to the
n=3 n = 3 -
Brackett Series: These are transitions to the
n=4 n = 4 -
Pfund Series: This series includes transitions to the
n=5 n = 5
- What was the purpose of Davisson and Germer experiment? Explains and analyse its results.
Original Purpose:
Accidental Discovery and Quantum Mechanics:
Experiment Details:
Results and Analysis:
-
Wave-Like Behavior: Instead of a random scattering pattern, Davisson and Germer observed a series of concentrated spots. These spots formed a pattern that resembled the diffraction patterns produced by waves, not particles. When the wavelength of these electron waves was calculated, it matched the theoretical prediction made by de Broglie for the wavelength of an electron.
-
Confirmation of de Broglie’s Hypothesis: This experiment provided the first solid evidence of de Broglie’s hypothesis of matter waves, suggesting that matter can exhibit wave-like properties, a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics.
-
Impact on Physics: The Davisson-Germer experiment’s findings were groundbreaking. They played a significant role in the acceptance of wave-particle duality theory and the broader development of quantum mechanics. This theory fundamentally altered our understanding of how particles at the atomic and subatomic level behave.
-
Brillouin Zones Analysis: Later analyses related the experiment’s results to the concept of Brillouin zones in solid state physics, further illustrating the wave nature of electrons and their interactions in crystalline structures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
You can access the Complete Solution through our app, which can be downloaded using this link:
Simply click “Install” to download and install the app, and then follow the instructions to purchase the required assignment solution. Currently, the app is only available for Android devices. We are working on making the app available for iOS in the future, but it is not currently available for iOS devices.
Yes, It is Complete Solution, a comprehensive solution to the assignments for IGNOU. Valid from January 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023.
Yes, the Complete Solution is aligned with the IGNOU requirements and has been solved accordingly.
Yes, the Complete Solution is guaranteed to be error-free.The solutions are thoroughly researched and verified by subject matter experts to ensure their accuracy.
As of now, you have access to the Complete Solution for a period of 6 months after the date of purchase, which is sufficient to complete the assignment. However, we can extend the access period upon request. You can access the solution anytime through our app.
The app provides complete solutions for all assignment questions. If you still need help, you can contact the support team for assistance at Whatsapp +91-9958288900
No, access to the educational materials is limited to one device only, where you have first logged in. Logging in on multiple devices is not allowed and may result in the revocation of access to the educational materials.
Payments can be made through various secure online payment methods available in the app.Your payment information is protected with industry-standard security measures to ensure its confidentiality and safety. You will receive a receipt for your payment through email or within the app, depending on your preference.
The instructions for formatting your assignments are detailed in the Assignment Booklet, which includes details on paper size, margins, precision, and submission requirements. It is important to strictly follow these instructions to facilitate evaluation and avoid delays.
Terms and Conditions
- The educational materials provided in the app are the sole property of the app owner and are protected by copyright laws.
- Reproduction, distribution, or sale of the educational materials without prior written consent from the app owner is strictly prohibited and may result in legal consequences.
- Any attempt to modify, alter, or use the educational materials for commercial purposes is strictly prohibited.
- The app owner reserves the right to revoke access to the educational materials at any time without notice for any violation of these terms and conditions.
- The app owner is not responsible for any damages or losses resulting from the use of the educational materials.
- The app owner reserves the right to modify these terms and conditions at any time without notice.
- By accessing and using the app, you agree to abide by these terms and conditions.
- Access to the educational materials is limited to one device only. Logging in to the app on multiple devices is not allowed and may result in the revocation of access to the educational materials.
Our educational materials are solely available on our website and application only. Users and students can report the dealing or selling of the copied version of our educational materials by any third party at our email address (abstract4math@gmail.com) or mobile no. (+91-9958288900).
In return, such users/students can expect free our educational materials/assignments and other benefits as a bonafide gesture which will be completely dependent upon our discretion.
Related products
-
IGNOU Assignment Solution
IGNOU MEG-19 Solved Assignment 2022-2023 | MEG | THE AUSTRALIAN NOVEL
₹101.00 Go to the App -
IGNOU Assignment Solution
IGNOU MEG-12 Solved Assignment 2022-2023 | MEG | A Survey Course in 20th Century Canadian Literature
₹101.00 Go to the App